- Why Facebook Marketing Slaps Twitter Marketing In the Face
- A Cool Wordpress Plugin to Integrate Facebook "Like" Functionality
- Local Search Recipe: Making KML Files and GEO Sitemaps Are a Piece of Cake.
- Crawling and the real time web
- Competitive Intelligence in SEO & Social Media
- More Recent Articles
Why Facebook Marketing Slaps Twitter Marketing In the Face
And beats its pants off. [Sorry we were just brainstorming linkbait titles about John Daly's pants.]
I was asked to speak about "Capitalizing on the Twitter Revolution" at Pubcon. So I talked about Facebook.
Why?
I said: "Twitter revolution? Didn't that happen in 2008?"
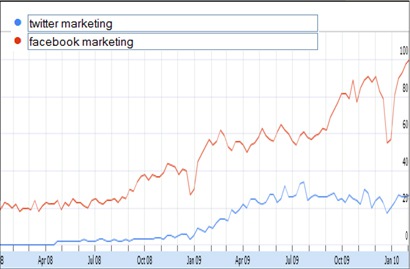
The following chart shows Twitter really taking off in 2009, but…
But Twitter was a lot cooler in 2008 when it was smaller. And the following chart shows something very interesting about Twitter for marketers:
Interest in Twitter marketing grew in the first half of 2009 but has stagnated since.
In my work with TweetROI, I've monitored what people tweet on phrases like "twitter marketing" and most of what I saw was the spammiest, lowest quality Internet Marketing- hypey new product cut-and-run strategies and lazy, uncreative tweet promotions.
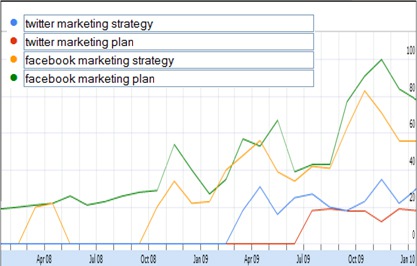
Also look at this:
The volume is lower and the lines more volatile, but Twitter marketing is clearly losing to Facebook marketing and stagnating.
Why is this happening?
Yes,I have enjoyed Twitter's geekiness. I have no problem with @ symbols or formulaic syntax. But not everyone in the U.S. or the World is like that.
Oh yes, the mainstream people.
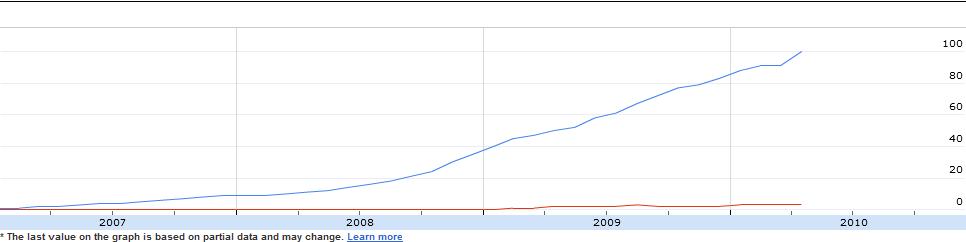
That's why the Twitter/Facebook comparison looks like this:
Facebook truly dwarfs Twitter. And yet the corporate search/social industry talks WAY more about Twitter. And there was a session devoted entirely to Twitter at Pubcon, but no session about Facebook. Alison Driscoll, to my knowledge, is the only other person who talked about Facebook.
Why Do Geeks Prefer Twitter?
Perhaps because everyone in the industry, like me, was avoiding Facebook and enraptured by Twitter. And because there weren't as many public case studies of Facebook marketing success as there were for Twitter.
Is this fundamentally fallacious? Twitter had great synergy with writers – the press, and bloggers – so it was more scrutinized and buzzed up.
Facebook is multimedia and holistic but dare-I-say "common". It's easier to be condescendingly expert on Twitter's side than Facebook's.
So as is typical for me, I'll buck the trend.
Here are 5 Reasons Facebook Marketing Slaps Twitter Marketing In The Face:
- Huge Penetration: As the search volume Insights charts show, Facebook is more popular, and Twitter marketing is stagnant.
- Reliable Stats: Facebook's built-in engagement stats rock, they tell you what FB cares about, and they won't just disappear any old day like a third party Twitter app might.
- Ad Integration & Targeting: Facebook ads are a powerful synergistic way to add power to your FB page, and their targeting ability ROCKS.
- Mainstream Appeal: Facebook is multimedia – pictures and video – and if you didn't notice, people like TV better than books. Facebook is more engaging and intuitive for normal people. (No, geeks are not normal people)
- Braslow's Hierarchy of Awesomeness (see below): This classic marketing framework I created two weeks ago demonstrates the importance of brand. It's easier to brand with Facebook than Twitter. Branding is key in red oceans because it's the only thing your competitors can't copy.
In other words, right now if you ignore Facebook marketing, you're like a 1986 Sony fan ignoring VHS. I knew a guy like that and he was an alcoholic. In other words, you're an alcoholic geek. I'm kidding! I'm not saying Twitter is Betamax and going away, but you can't ignore what the mainstream prefers, unless you only market to internet geeks.
Check out my whole Twitter Marketing vs Facebook Marketing presentation on Slideshare- it's funny and it includes tips on how to get more page fans- oops I mean page likers.
Yeah I'd rather be a liker than a fan, wouldn't you? ;-p
Check out the SEO Tools guide at Search Engine Journal.
Why Facebook Marketing Slaps Twitter Marketing In the Face
A Cool Wordpress Plugin to Integrate Facebook "Like" Functionality
If you liked Facebook's popular "Like" functionality and want to engage your Facebook fan page users or just random Facebookers, you will love the plugin we are sharing today.
You may have noticed that since last week we have been giving our readers the ability to "like" our posts on Facebook. So here I am sharing the plugin that enables everyone to grab this functionality to their blogs.
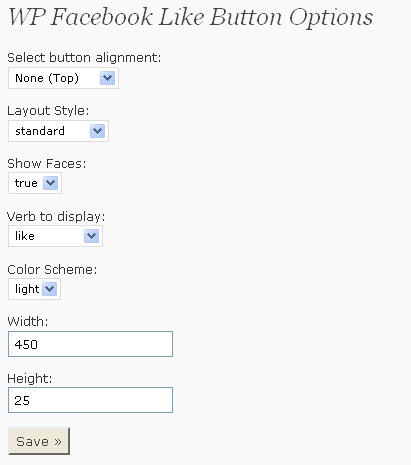
The plugin is called "Wordpress Facebook "Like" Button" – it is installed as a regular plugin and have a few options that help customize it. To access the options, browse to Settings->WP FB Like Button and there:
- Select button alignment:
- Choose the layout style;
- Select if you want the plugin to show the faces of Facebook users who liked a post;
- Set it to sound as "Like" or "Recommend";
- Choose the color scheme (either light or dark);
- Select the widget height and width:
Here's how the plugin looks like when you disable the count (this is what you see on SEJ currently):
Here's an example of how it might look if you enable the count:
The Like button enables users to make connections to your pages and share content back to their friends on Facebook with one click. This means if you click it, the update will be shared on your Facebook profile:
So far we are loving the plugin. It looks natural and seems engaging. What are your thoughts?
Check out the SEO Tools guide at Search Engine Journal.
A Cool Wordpress Plugin to Integrate Facebook "Like" Functionality

Local Search Recipe: Making KML Files and GEO Sitemaps Are a Piece of Cake.
Last month I shared one of my favorite recipes on tracking local search data with Google Analytics for wordpress. This month I figured that one of the most uncovered and "uncooked" areas in local search marketing is KML data and the use of Geo Sitemaps. So, I decided to put together a guide to help anyone who is struggling to understand how KML/GeoSitemap + local is a win- win….win.
Approximate Bake Time:
10 minutes
Ingredients
1 verified Google Webmaster Account
1 FTP uploader application
1 computer (Mac preferred. PC's tend to get sticky unless sprayed with Pam)
*½ glass of beverage
*2 slices of Dairy Queen Ice Cream Cake.
*Optional ingredients for optimal experience.
Background
First, it is important to understand what a few of these new words mean….
KML- Key Hole Markup Language (kml) is a file format used to display geographic data in an Earth browser, such as Google Maps and Bing Maps as well. You can create KML files to pinpoint locations, add image overlays, and expose rich data in new ways. KML is an international standard maintained by the Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc. (OGC).
Geo Sitemap- Google Geo Sitemaps is an extension of the Sitemap protocol that enables you to publish geospatial content (geo content) to Google, in order to make it searchable in Google Earth and on Google Maps. With Geo Sitemaps, you can tell Googlebot about your geo content, rather than waiting for Google to discover it "in the wild".
Directions
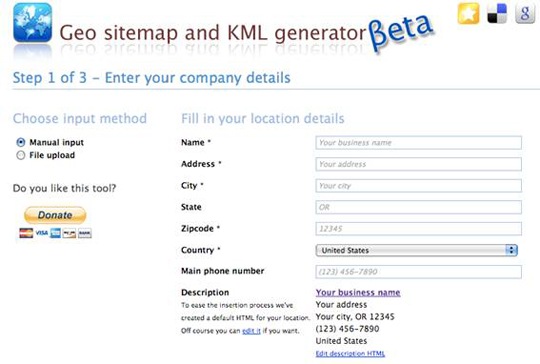
1. Go to GeoSitemapGenerator.com, which is a free (and amazing) tool that allows you to plug in the needed information and then download your very own copy of a geositemap and kml file.
If you have a ton of locations (more than 10) that you are submitting for your given business then choose the file upload option. You will then be given instructions on how to format .csv sheet to correctly upload the data. I have used this for uploading over 600 locations and it works like a charm.
- Fill in the correct business information. This is where you have to be exact. Your N.A.P. (Name, Address, and Phone Number) are the foundation of local search so make no mistakes! Once you have the correct information move on.
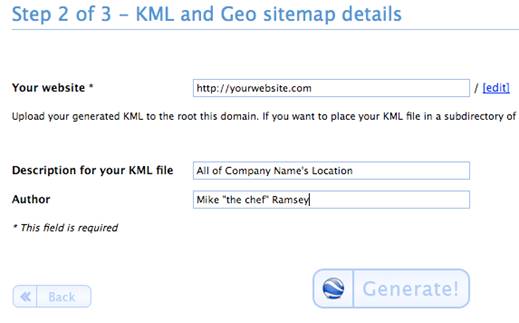
- Fill in the website details of the site that you are going to be uploading the kml file and geositemap to. Make sure that you edit the name of the .kml file.
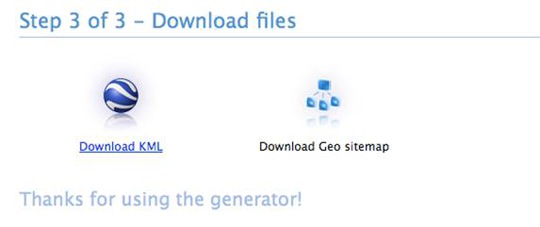
2. Download Both the KML file and the Geositemap, and upload them to your site.
For this you are going to be using your FTP uploader of choice. Wherever you put the file extension of your KML data will determine where you need to upload these files to. Generally they are on the main level of the site so you will be uploading them into the root folder and the URL's will look like this…
http://yourwebsite.com/geositemap.xml
http://yourwebsite.com/locatioin.kml
3. Check the links to make sure that the data is showing correctly.
Your Geositemap should look like this…

And your .KML file like this…
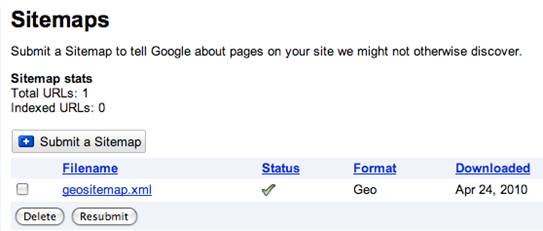
4. Submit your GeoSitemap to Google Webmaster to help your nearest GoogleBot find your location. You will need to log into your Google Webmaster account, and then click on "Site Configuration". You will see that "Sitemaps" is a drop down option offered, once clicked on you will be able to add your geositemap like in the picture below.
Summary
If you have followed the above directions then you are now set with your kml and geositemap data uploaded to your website. Also, since you took the time to read to the end of the post, you now get to find out the secret ingredient of why these files are so important for local.
Local Search Rankings are all about location prominence. The better your case in proving that your name, address, phone number, and other business data is correct… the better chance you have at ranking well. So, in dealing with KML data, you are confirming that your information is correct and going the extra mile to do so while notifying search engines.
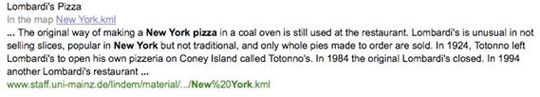
If you are lucky, your KML data will get indexed and show up in the User Content tab on a Google Places page like this one below for Lombardi's Pizza in New York.
When that happens, you let me know and we can eat our cake and laugh at non KML'ers together from a lofty tower.
Check out the SEO Tools guide at Search Engine Journal.
Local Search Recipe: Making KML Files and GEO Sitemaps Are a Piece of Cake.
Crawling and the real time web
It's all about happiness metrics
A while back I wrote here about how search engines go about discovery, the act of finding your pages. I thought we should continue that with a look at how they crawl and index them as well. With a twist, we're going to discuss the uber fast world of real time.
Over the last while we've seen a distinct interest in search for social and so-called real time search. Actually, even efforts to index the web at ever increasing rates has been a mainstay for many years now (remember when Google refreshed once/month? Unheard of these days). To that end (infrastructure) we can look at the latest effort; Caffeine.
There is a decided need for speed that is evident in many areas including;
- Caffeine
- Pubsubhubub
- Social (for discovery)
- RSS from any page
- Page load speed (?)
You get the idea. One thing that one has to consider when it comes to processing is to enable systems that are optimally efficient. The real problem comes in deciding what is and isn't important to people in 'real time'.
Search engines need to look at;
- Cost of crawling
- Re-fresh rates
- Query space freshness requirements
- Value of changes
- Content type
It is certainly an interesting discussion and one that is part of, if we realize it or not, our collective futures (as search marketers and people). One problem we often see in the search space I that we're more reactive than pro-active. We see all of this evolution around us, but seldom go below the surface.
Start your engines
Now, since we're warmed up, let's take a quick look at Greg Linden's post; Re-crawling and keeping search results fresh – and in particular;
"The core idea here is that people care a lot about some changes to web pages and don't care about others, and search engines need to respond to that to make search results relevant."
So, search engine folks need to consider not only the 'if' and 'when' it is crawled/indexed, but where and how they are returned, re-crawled etc… (especially in heavy universal situations). But at the same time crawling all the pages of the web is inefficient and costly.
In the case of real time, or even the regular index, the update frequency is going to be a huge consideration. Websites that are active, tend to have higher crawl rates. This means we should have a strong content strategy in place if we want to make the most from the new speeder search engines.
The real time web puts a premium on discoverability and indexation. This means, as discussed before, adopting more push technology in your efforts is likely a good idea. A few of the aspects that search engines (such as Google) look at are;
- Trigger Events – this would be elements such as hot news, query analysis that set off the actual event for indexing/displaying results.
- Quality Signals – establishing a Trust/Harmonic Rank type of concept for links in social (trusted domains etc a la OneRiot)
- Update Frequency – obviously consistency would play a roll in how often a page is visited (and hopefully indexed).
It is certainly evident that search engines are going to have to find not only better signals to make decisions that produce a valuable result, but find ways to create inclusion/interfaces that better attract users.
The future of real time search
This all does seem to point to the fact that we're not quite there yet. But let's continue the trail and see where it leads.
The next consideration we need to take in is that efficacy of the information being presented. The obvious element here is going to be the more fluid data points. What one Googler said they refer to as 'Happiness Metrics'. These are the user metrics such as query analysis, click data and other forms of implied user feedback.
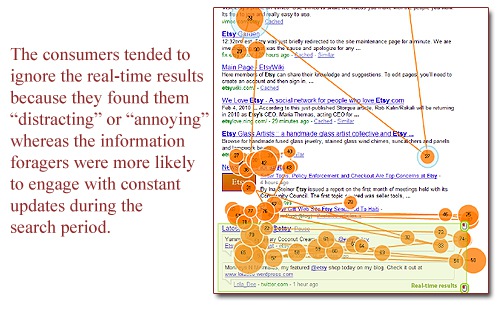
But the question remains, how much value to RTS results have? In a recent study done by One Up Web, they discovered;
- 73% had never heard of real-time results before participating in this study
- Only a quarter of the consumers cared for the real-time results compared to 47% of the information foragers
- The majority of the participants surveyed were indifferent to the real-time results
- Yet, we also know that consumer choices are influenced by their social graph. But interestingly enough, it was the consumers that were least interested in the social component of the real-time results.
- The consumers tended to ignore the real-time results because they found them "distracting" or "annoying" whereas the information foragers were more likely to engage with constant updates during the search period.
One thing that comes to mind is finding some type of popularity measure for the social world. Or, taking it to a more granular level with personalization. It stands to reason that users that are like-minded will produce more usable results. At this point the real time and social search realms are divided. I'd have to believe some type of hybrid, inclusive of a personalization aspect, would be the future of RTS.
To some degree at least (combining user feedback signals with the social graph).
Grab and Hold
If it's for real time search, news or just a faster regular index search, speed is a concept worth noting for SEOs.
If you've ever played 'grab and hold' with the QDF (query deserves freshness) then you would be familiar with velocity concepts. If you haven't, let's review. This analogy comes from military concepts of taking a piece of land and holding it. For our purposes, we're looking to get a foot hold with temporal advantages, then maintain the ground we've gained.
If you've ever noticed a relatively new page that ranks early one, but degrades over (a short period of time), then you've seen it in action.
Getting the most from RTS is often much the same, though not as stable. You will want to have all your ducks in a row from SEOs to PR peeps and Social Media depts. Given the flux and temporal nature to RTS, this is at a premium. That combined with what we know of trust signals, is a natural part of any RTS targeting component.
It's a pushy kind of world
And so we, as SEOs, need to start to consider not only how push technologies work, but the (potential) evolution of the world of real time search. It is part and parcel to any universal search strategy. We need to get in tune with the PR and social peeps. But do we need to do it now??
Nope… not really. In the current incarnation it is the least of my worries as far as universal search strategies are concerned. We're much better off looking at verticals such as news, video and shopping. I do think it is something we should be watching as it has the potential to become a valued segment in the near future. Besides, understanding how to make the most of push technologies, syndication and visibility in the modern age of need for speed, will only help us in the long run.
On a side note, as I tried to actually get some RTS results on Google as I wrote this last night, it seems to have been scaled way back. It took some Twitter trending terms to actually produce one. This seems to speak to how valued it is in the current SERP landscape.
Anyway, I hope you enjoyed this little adventure, and if you have questions on crawling or thoughts on real time search – please do sound off in the comments.
Resources
As always, I have some interesting patents for those looking to dig deeper into the various methods used in crawling/indexing;
Googly Patents
- Duplicate content search
- Method and system for query data caching and optimization in a search engine system
- Search result ranking based on trust
- Multiple index based information retrieval system
- Systems and methods of synchronizing indexes
- Duplicate document detection in a web crawler system
Microsoft Patents
- Using core word to extract key phrases from documents
- Mining information based on relationships
- Acquiring web page information without commitment to downloading the web page
- Classifying search query traffic
Yahoo Patents
- Segmentation of search topics in query logs
- Systems and methods for search query processing using trend analysis
- Optimizing ranking functions using click data
- System for refreshing cache results
Check out the SEO Tools guide at Search Engine Journal.
Crawling and the real time web
Competitive Intelligence in SEO & Social Media
Understanding thy competition is a golden rule in any kind of business, ranging from online marketing to politics to running the local mom & pop corner grocery store.
Joanna Lord has put together a pretty good wrap up of competitive intel tracking and signals over at SEOmoz this morning : Competitive Intelligence: Purpose & Process, with an emphasis on the evolution and growth of a brand or business. In the current economic rebound and online marketing landscape where new outlets like Facebook (let's face it, Facebook is the Internet for A LOT of normal Americans), Foursquare and Twitter along with new emerging social and search oriented trends and disciplines such as guest blogging, blogger outreach and integrated PR strategies, brand evolution in competitive intel is a fluid and dynamic field.
As marketers, the idea of pausing is equated with losing momentum which scares the hell out of us all. This industry moves too quickly, and pausing to reflect on where your brand is compared to your competitors seems like time poorly spent.
Lord builds upon this with an emphasis on tracking such momentum and trending, with Product Growth & Benchmarking
This is perhaps the most time consuming element to competitive intelligence when it is done well. There needs to be someone in charge of competitive intelligence maintenance. This person should subscribe to your competitor's blog so you are hearing about product launches as they happen, and all company announcements in real time. You can also gain a lot of insight from reading the comments to those posts.
In addition to this you should set up Google Alerts for your competitor's brand plus the words "launches" and "announces." We all know that Google Alerts are limited and somewhat unreliable, but you should have a daily digest set to notify you of any big moves your competitor's are making. You never know which could be a real momentum changer.
I work with a lot of brands that are either established in their vertical, or that I have assisted to establish and quite frankly, while I always have one eye on what's ahead and am consistently On To the Next One, its always smart business to keep one eye on the rear view mirror, to see who's gaining ground on you, what they are doing, and how you can pull the rug from underneath them or crush them.
I suggest giving the SEOmoz post a good read, and also, would like to reprint some competitive intelligence tactics that I previously put together here on Search Engine Journal that will also be helpful.
Understanding what your competitors are doing online is a must and absolute priority when launching a new website that is entering a competitive space and also when established websites want to keep an eye on their competition. By knowing what your rivals are doing in their SEO and social media space, not only will you have a better knowledge of their online marketing strategy, but you can also emulate what is working for them, and generate internal ideas to stay proactive.Furthermore, by understanding what your competition is doing in terms of on-site SEO, link building, social media marketing, developing third party properties and other search marketing tactics; you can also identify potential new threats which are making it up the rankings and also unearth tactics which are working from them (or not working for them), that you can improve upon, and thrive from in your overall marketing strategy.
And doesn't everyone love playing spy every once in a while?
Identifying the Competition
The first step in identifying your online competition is checking out the search results for your most popular keywords. Do not look only at keywords which drive the most traffic, but also your longtail keyterms and also the keyterms which convert the most sales, leads or phone calls.
By comparing the sites which you compete with in these various groups of keyterms, you will more or less identify different styles of competition that you can learn from and monitor. Here are some types of sites which may not appear for your basic keyterms in the serps, that you need to monitor.
- Affiliate sites are your competition. Not only sites which run the affiliate ads of your rivals, but also your own affiliate ads, because if they are ranking above your company's site, they are taking money out of your pocket (or the search division's pocket) by driving traffic and sales that you should be driving. Furthermore, affiliates don't have to deal with internal regulations and beauracracy, so they can more or less get away with more tactics like publishing loads of content, paid linking, and taking full advantage of the social media outlets your management or PR division is not letting you tackle. Affiliates are the ninjas, mercenaries and dark armies of your industry, learn from them.
- Offline competitors sometimes don't do the best SEO, maybe they just launch a flash site or brochure page and don't rank at all, but they may have an advertising agency with a massive creative team building up their social media presence, hold contests or sweepstakes, build up Facebook followings, have a massive PPC budget and spend a lot of money on site advertising and sponsorships. By monitoring what the do in online advertising, you can identify keyterms and copy which work for them in their PPC campaign and also find out the sites or networks where they are serving graphic advertising, and contact those same networks about striking a deal which will assist with your SEO or linking. If your competition is serving ads there, then those sites hit your target market.
On-Site Competitive Intelligence
Now that you have identified the sites you need to monitor as part of your competitive intel strategy, now start looking into the on-site factors which help them rank in the search engines. You may find not only what they are doing right, but what you are doing wrong. When performing a competitive intel report, I suggest including your own site in the report and even having a third eye, like an SEO consultant or internal staff member, do the research on your own site.
- Site URL Structure : By tracking the URL structure and file naming structure of competitors, you can determine the best route to gain a competitive advantage over other companies.
- Site Development and Coding Structure : Which language is the site being coded in. Are there any conflicts in programming language or separate IP's? This information is vital to SEO competitive intel.
- Use of Analytics : Is the competitor tracking user behavior and referrals via Google Analytics, Hitbot, Omniture? Looking into their analytics systems help give an idea of how much information they are capturing from their visitors and how advanced their internal tracking is – which may define how advanced their SEO team is.
- The directory files and URL structures of listings pages : This will be used to determine which techniques these competitors are using for their individual pages, their content, meta and URL structures, and how these reflect in the Google, Yahoo and MSN rankings.
- Page Title and META Title Review: Page titles are one of the most influential HTML elements used in an optimization campaign. Since the optimization of this variable is connected to rankings and actual links in the Search Engine Results Pages (or "SERPs"), an analysis has been conducted to provide which sites use a preferred title structure and which just use repetition of their company name.
- META Tag Review (Description / Keywords): META tags have limited relevance to rankings, but do play a part in that search results often feature the META Description tag. Knowing this, an optimized description that instigates action from the searcher is preferred. Further, integrating the targeted keywords allows for them to be bold or otherwise emphasized in the listings – which helps to convert more clicks in the SERPs through to the optimized site.
- Navigational System Review: Search engines spider, or seek out new content based on the links they find to resources on a page. Navigation systems are the most consistent manner for building internal link popularity, so research evaluates the overall strength of these systems used. For example, a Flash based navigational system is horrible for SEO, whereas consistent keyword driven links with keywords integrated are optimal.
- Broken Links : If a site has broken links, broken files or lists non-existant pages, then Google will lower the ranking of that site because the engine believes that the site is under construction. Run a link check using Xenu Link Sleuth to see if your competition is overlooking such linking and internal navigation issues.
- HTML Code Validity: Using the W3C Validation tools, your competitors'' web sites have been reviewed. This allows the engines to promote sites that deliver a consistent and predictable user experience. Run each site through the validation tool, and reported back the number of errors noted.
- Design & SEO Integration: Similar to the internal navigational structure, the use of some HTML elements are preferred over others for SEO purposes. Our research and analysis of competing site designs have been provided in this document.
Offsite Competitive SEO Elements
Not only do onsite tactics assist with the ranking of a website, but sometimes more importantly offsite tactics can benefit the competitive advantage to boost a site from the bottom of the front page on Google, to the top three traffic driving positions.
By monitoring offsite SEO tactics, and social media tactics, you can get a rounded feel for the link building strategies your competitors are using, their participation in blogs, sites they may own which are harnessing social media equity and directing it to their main site, if paid linking is working for them, and how they're doing on Delicious, Digg and in vertically targeted social networks. All of these factors have a direct influence on search engine rankings and you will not only learn what your competition is doing, but what they are not. And by identifying these holes, oversights or even genius ideas … and applying them to your marketing strategy, you can further excel within your industry.
- Local Listings : Determine the local SEO listings that your competition has made on Yahoo Local, Citypages, BOTW Local, MSN Live and other local search engines or local profiles. These differ from the results shown in organic web search sometimes and can be an indicator of local seo techniques used or overlooked by the competition.
- Number of Inbound Links: Using Yahoo! Site Explorer, report on the number of inbound links to each of the analyzed web sites. As a rule, the more links and the more relevancy – the better. Search Engines like Google use inbound links to help shape the overall level of authority of a web site.
- Linkbait or Viral Marketing : How are these competitors building links? Are they running link baiting programs and actively having articles submitted to Digg & StumbleUpon? Are they using any Viral Marketing techniques like videos, widgets or badges which link back to them and assist with their rankings. Dig into their campaigns to find out what they are using, and monitor the social networks to identify future social linking campaigns.
- Social Media : Do they actively use social media to market their business? Does their company have a Wikipedia page? How do they rank for their own brand name and are social profiles served in these results? Have they even secured their brand across social networks? Do they distribute online video? This research will help determine a social media plan and also identify competitive advantages that you can use to your advantage.
- Blogging : Do these companies blog and who is doing their blogging? Are the blogs on a subdomain, a whole other website or in an internal directory file. How often do they post? How many subscribers will they have? This information will assist you construct your blogging strategy and possibly unearth some ideas.
- Paid Link Research: It is difficult to say with certainty that an inbound link has been purchased. There are however signs where common systems like Paid Directories and Link Networks are used on a site. Research of inbound, paid links to your competitors from sidebars, ads on newspaper sites or bad paid linking in footer links may give you some insight as to which anchors they are targeting and what is working for them.
- Site visits and Traffic : Using a mix of data from Alexa, Compete and other web traffic estimation tools, estimate the traffic of the competitors in terms of visitors, time spent on site, top referrals and other information driven by third party tools.
- Page Rank and other Metrics : Compile a list of competitive metrics including Google PageRank, SEOmoz PageStrength, Delicious Bookmarks, StumbleUpon voting, Google Page Indexing, Google Competitive Indexing.
- Competitive Rankings : Last but not least, run a ranking check using a search engine friendly software for each of the terms which you have determined for targeted SEO keyterms via your comeptitive research. Check the rankings for these sites and terms in Google, Yahoo, Ask.com, Bing and maybe some engines which are used specifically by your industry.
This may sound like a lot of information to monitor, and you'll probably want to add more industry specific metrics to your research dependent upon how SEO savvy your market is. But in the long run by documenting this information now, and revisiting it once a quarter, you will have a pinpoint idea of the tactics your search rivals are utilizing, what they are not, and even what they are picking up.
I also recommend monitoring their listings on Monster.com and other job search engines to identify the internal positions they are hiring for or have, like SEO Manager or Social Media Marketing Assistant, this way, you may gather some insight as to what they are planning in the future, which may assist you with getting the internal go ahead from your CEO or CMO to embark on a smart social media campaign, before the competition does.
If you need any help with the tools needed to perform a lot of this research, please contact me via email or Twitter (in my profile box at the top of this post) or check out our SEO Tools post for some ideas.
Are there any other competitive intel tactics you recommend? Please feel free to share them in the comments below.
Check out the SEO Tools guide at Search Engine Journal.
Competitive Intelligence in SEO & Social Media
More Recent Articles

Click here to safely unsubscribe now from "Search Engine Journal" or change your subscription or subscribe
Unsubscribe from all current and future newsletters powered by FeedBlitz
Your requested content delivery powered by FeedBlitz, LLC, 9 Thoreau Way, Sudbury, MA 01776, USA. +1.978.776.9498
sábado, 1 de mayo de 2010
Suscribirse a:
Enviar comentarios (Atom)
Seguidores
Archivo del blog
-
▼
2010
(127)
- ► septiembre (7)
-
▼
mayo
(20)
- 6 new articles
- 2 new articles
- 6 new articles
- 4 new articles
- new articles
- 7 new articles
- 5 new articles
- 4 new articles
- 7 new articles
- 4 new articles
- Search Engine Journal - 5 new articles
- 5 new articles
- 4 new articles
- 2 new articles
- Search Engine Journal - 6 new articles
- 3 new articles
- <!-- AOL_MESSAGE --><!-- Your FeedBlitz Updates ...
- <!-- AOL_MESSAGE --><!-- Your FeedBlitz Updates ...
- <!-- AOL_MESSAGE --><!-- Your FeedBlitz Updates ...
- <!-- AOL_MESSAGE --><!-- Your FeedBlitz Updates ...








No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario